“Discover the key differences between cloud hosting vs traditional hosting. Learn about scalability, cost, performance, and security to choose the best option for your website or business.”
Table of Contents
Introduction
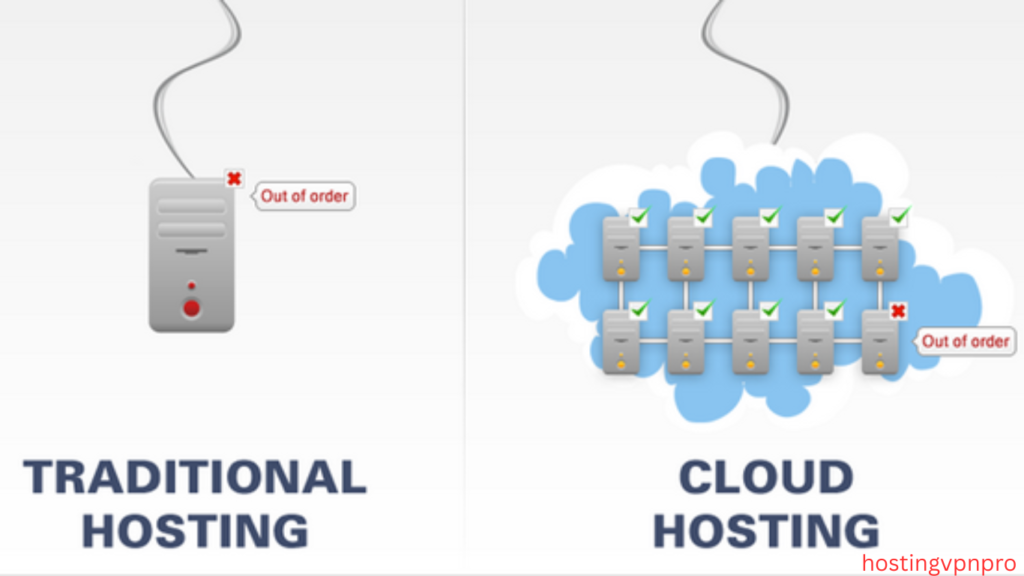
When it comes to hosting your website or application, choosing the right hosting solution is crucial. Cloud hosting and traditional hosting are two of the most common options, each offering unique advantages and challenges. While traditional hosting relies on physical servers and fixed resources, cloud hosting takes advantage of virtualized resources distributed across multiple servers, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
In this article, we’ll compare cloud hosting and traditional hosting across various factors like cost, performance, scalability, security, and ease of use, helping you make an informed decision on which option is best suited for your needs. Whether you’re running a small personal blog or managing a large-scale enterprise website, understanding these differences can make a significant impact on your online presence and performance.
Cloud Hosting vs Traditional Hosting
When deciding between cloud hosting and traditional hosting, it’s essential to understand the fundamental differences that can impact your website’s performance, scalability, and costs. Both hosting types have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the specific needs of your website or business.
1. What is Traditional Hosting?
Traditional hosting typically involves a single physical server where all of your website’s files, databases, and content are stored. This server is usually managed by a hosting provider and allocated a set amount of resources like CPU, memory, and storage. There are different types of traditional hosting, such as:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share the same server resources.
- VPS Hosting: A private portion of a server is assigned to your website.
- Dedicated Hosting: Entire server resources are dedicated to your website.
While traditional hosting offers simplicity, it comes with limitations in scalability and flexibility.
2. What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting, on the other hand, utilizes multiple servers connected in a network to host your website’s data. These servers are often distributed across various data centers, allowing the hosting platform to scale dynamically and provide better performance. The key benefits of cloud hosting include:
- On-Demand Resources: You can scale resources up or down as needed.
- High Availability: Your website’s data is stored across several servers, reducing the risk of downtime.
- Pay-As-You-Go: You only pay for the resources you actually use.
Cloud hosting provides more flexibility and reliability, especially for websites with fluctuating traffic demands.
3. Key Differences:
a) Scalability:
- Traditional Hosting: Limited by the physical resources of a single server. Once those resources are maxed out, you’ll need to upgrade or migrate to a more powerful server.
- Cloud Hosting: Highly scalable. You can increase or decrease resources like CPU, storage, and bandwidth without any significant downtime. Cloud hosting automatically adjusts to traffic spikes or drops.
b) Performance:
- Traditional Hosting: Performance can suffer if multiple websites share the same server (as in shared hosting), or if the server’s hardware becomes outdated.
- Cloud Hosting: Offers better performance, as resources are distributed across multiple servers. If one server fails, the system can switch to another without affecting your website’s availability.
c) Reliability:
- Traditional Hosting: Relies on a single server, so if the server goes down, your website experiences downtime.
- Cloud Hosting: Due to its distributed nature, cloud hosting offers high availability. Even if one server fails, the others can continue to handle the traffic.
d) Security:
- Traditional Hosting: Security depends on the server’s configuration. Dedicated hosting can offer robust security but may require more management and expertise.
- Cloud Hosting: Generally offers more advanced security features, such as automatic backups, DDoS protection, and the ability to isolate workloads. However, because cloud hosting is accessed via the internet, there may be additional concerns around data breaches.
e) Cost:
- Traditional Hosting: Typically cheaper upfront, especially with shared hosting. However, you may face higher costs for upgrades, bandwidth overages, or additional resources.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting tends to have a flexible pay-as-you-go model, which means you only pay for what you use. However, costs can vary widely depending on usage and the services you choose.
4. Which One is Right for You?
- Choose Traditional Hosting if you have a small website with limited traffic and need a budget-friendly option. It’s ideal for personal blogs, small businesses, and websites with predictable needs.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if you need flexibility, scalability, and reliability. It’s well-suited for websites with variable traffic, businesses that are growing, or applications requiring constant uptime and performance.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between cloud hosting and traditional hosting comes down to your website’s requirements. If you’re looking for a reliable and scalable solution with room for growth, cloud hosting is the clear winner. However, for smaller, less complex websites, traditional hosting can still be a cost-effective and straightforward option.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between cloud hosting and traditional hosting?
Cloud hosting uses multiple servers to host your website, allowing for better scalability and flexibility, while traditional hosting relies on a single physical server. Cloud hosting offers higher reliability and performance, whereas traditional hosting is more cost-effective for smaller websites with consistent traffic.
2. Is cloud hosting more expensive than traditional hosting?
Cloud hosting can be more expensive depending on usage, as it typically operates on a pay-as-you-go model. However, traditional hosting may have hidden costs for upgrades, resource overages, or higher performance servers. The overall cost depends on the specific needs of your website.
3. Which hosting option is better for a small business?
For a small business with predictable traffic, traditional hosting (like shared or VPS hosting) may be sufficient and more affordable. However, if your business expects growth or fluctuating traffic, cloud hosting offers scalability and flexibility to handle traffic spikes without downtime.
4. Can I easily upgrade my hosting plan with traditional hosting?
Upgrading a traditional hosting plan may involve migrating to a new server or service type (e.g., moving from shared hosting to a dedicated server). Cloud hosting, on the other hand, allows for seamless resource upgrades without downtime, making it easier to scale as needed.
5. Is cloud hosting more secure than traditional hosting?
Cloud hosting generally provides better security due to its distributed infrastructure, automatic backups, and advanced features like DDoS protection. Traditional hosting, while secure, often requires manual security configurations and may be more vulnerable to downtime if the server is compromised.